All rapid prototyping technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages. Each technology can cover limited areas of application. It is therefore of crucial importance which requirements are placed on the component to be manufactured. Only when you have questioned this exactly can you determine the optimal technology for the creation of the component. Here is a brief overview of what distinguishes the individual 3D printing technologies from each other.
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)

Advantages: mechanically resilient, no support structures are required, high component density, the most complex shapes possible, thermally and mechanically resilient, very fast manufacturing process.
Disadvantages: slightly rough surface, only single-color models are possible.
Material: Polyamide – PA12.
Powder printing – Powder printing – (3D Printing – 3DP)
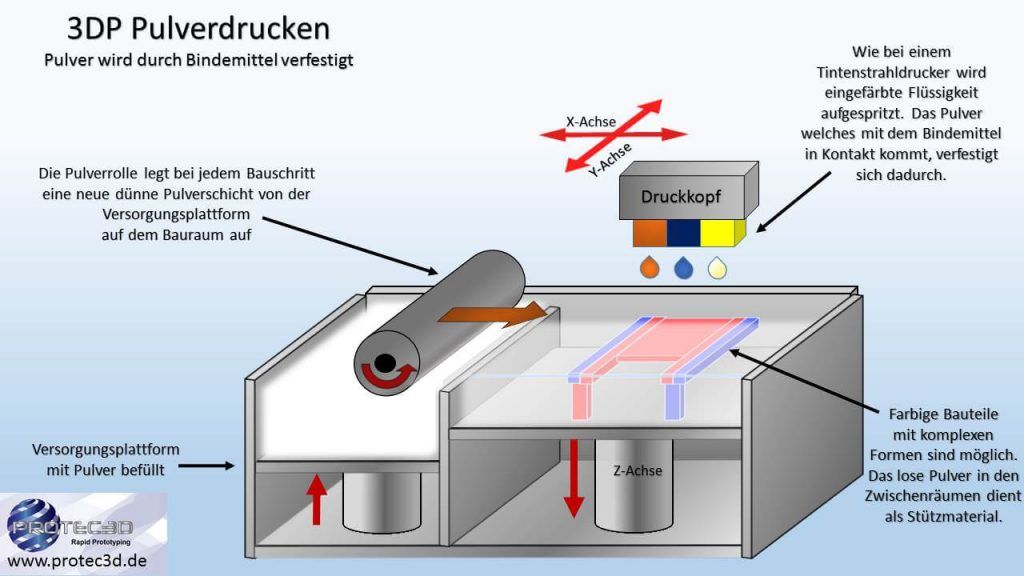
Advantages: Fast production, no support structures are required, full-color models can be displayed, the most complex shapes are possible.
Disadvantages: mechanically only partially resilient if the components are post-treated with composite materials, slightly rough surface such as sandblasted.
Material: specially treated homogeneous powder reinforced with composites.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
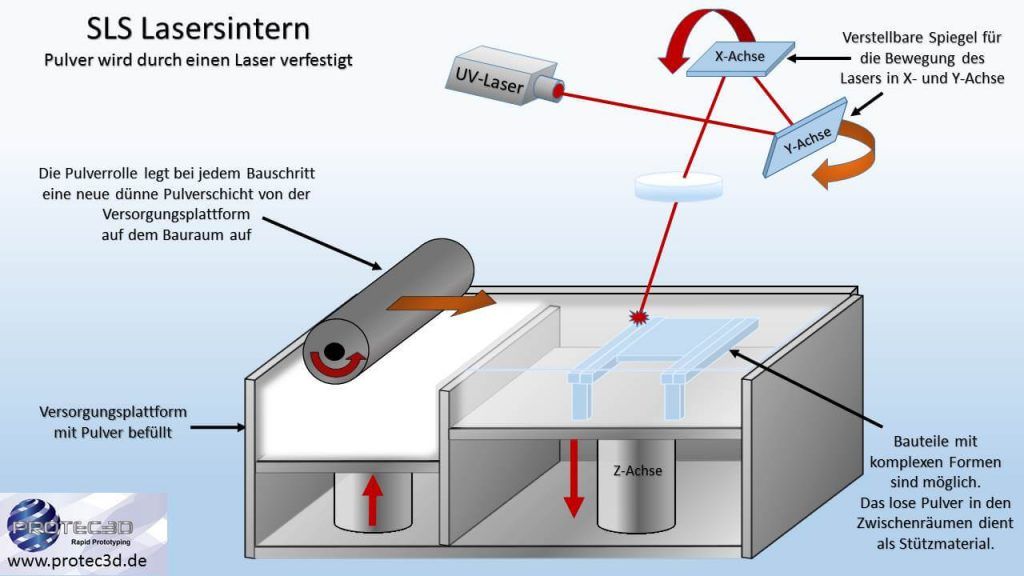
Advantages: mechanically resilient, no support structures are required, flexible components, variety of materials, the most complex shapes possible, thermally resilient.
Disadvantages: slightly rough surface, slow manufacturing process, only single-color models are possible.
Material: Different polyamide mixtures. (PA2200, PA12MD, etc.)
Stereolithography (SLA)
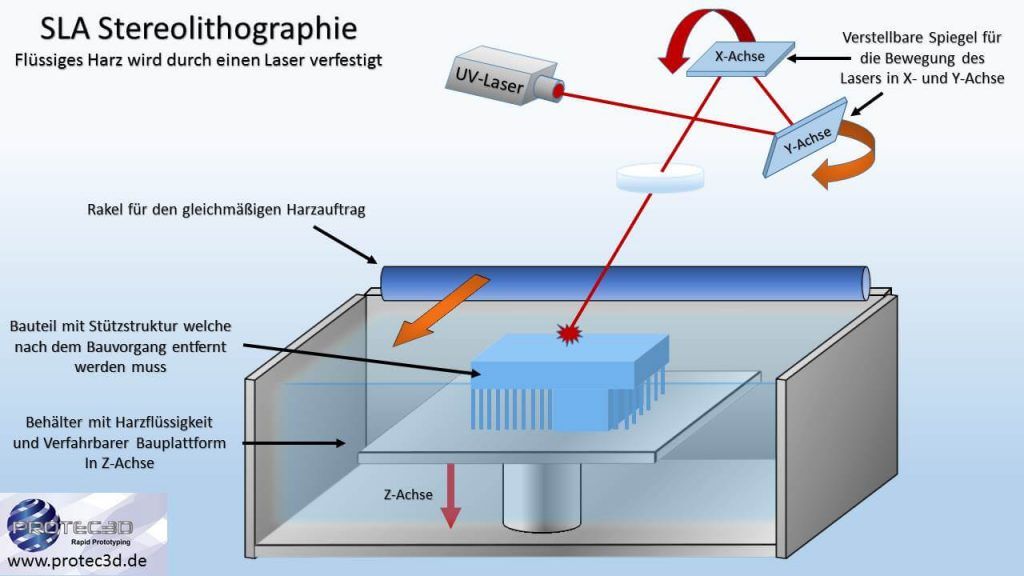
Advantages: very detailed and fine surface, partially mechanically resilient, high manufacturing accuracy, transparent components are possible, the most complex shapes possible.
Disadvantages: Only UV-curable plastics/resins can be used, high manufacturing costs, only single-color models are possible, slow manufacturing process, not all materials are thermally resilient. Not all geometries can be produced without problems, as support structures have to be removed afterwards.
Material: Plastics and resins which harden under UV light or heat.
Fused deposition modeling (FDM with a nozzle)
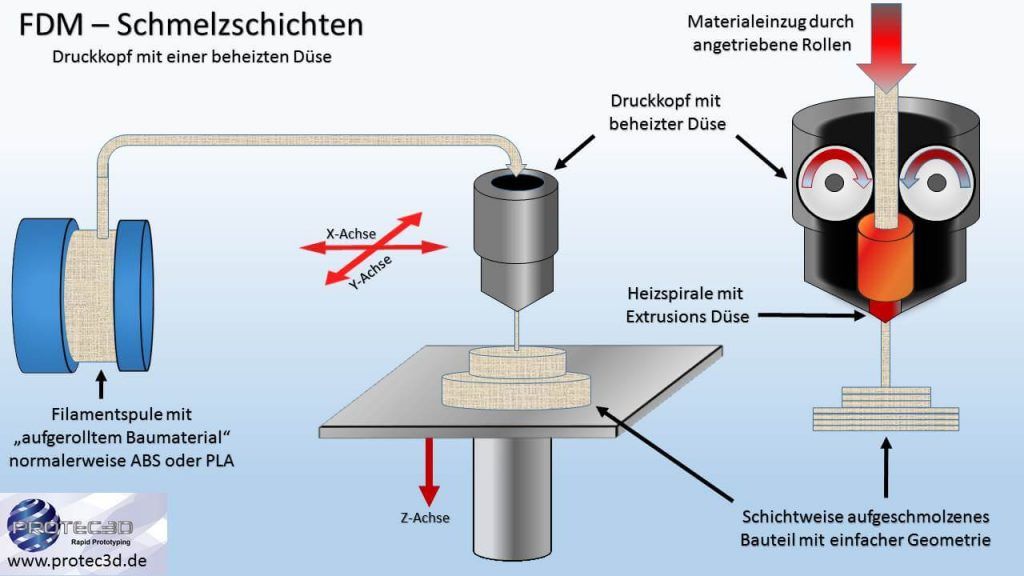
Advantages: inexpensive, resistant components are possible.
Disadvantages: Only surfaces with grooves are possible, average manufacturing accuracy, only single-color models are possible, supporting structures and reworking are necessary, very slow manufacturing process.
Material: Thermoplastics such as PVC and ABS.
Fused deposition modeling (FDM with two nozzles)
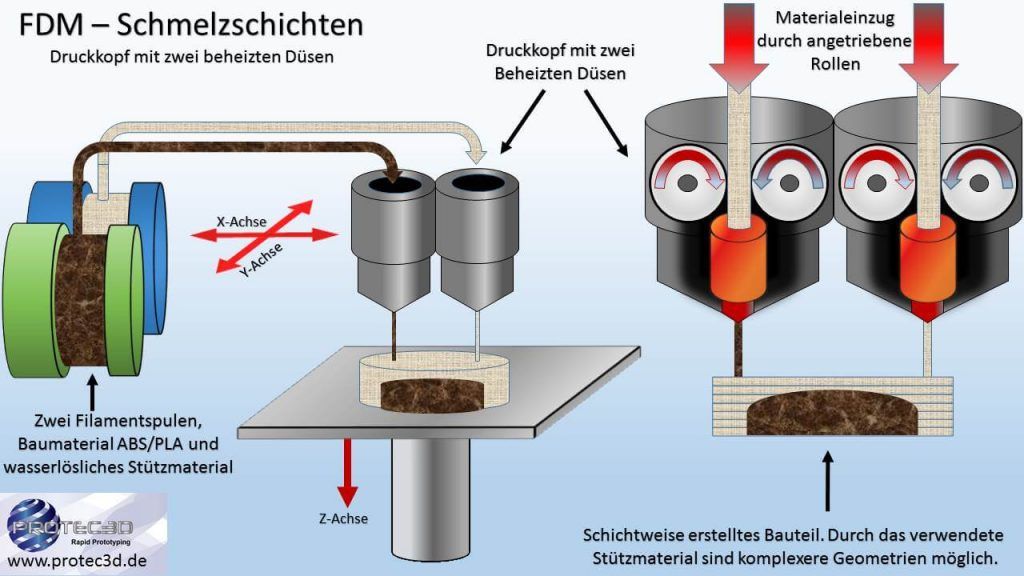
Advantages: inexpensive, resistant components are possible.
Disadvantages: Only surfaces with grooves are possible, not multicolored, slow manufacturing process.
Material: Thermoplastics such as PVC and ABS.
Polyjet method (Multi-Jet Modeling – MJM)
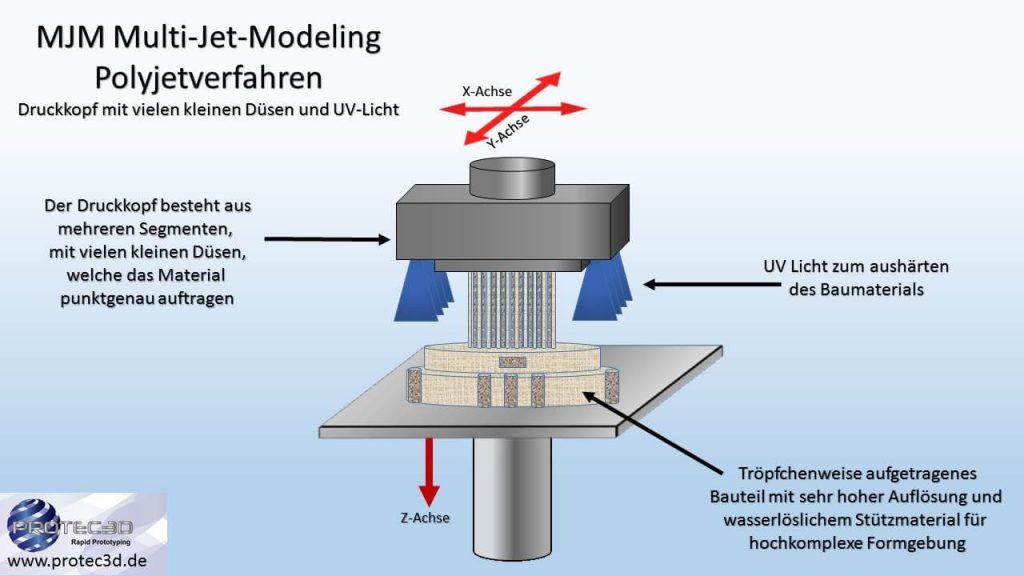
Advantages: high accuracy, very smooth surfaces are possible, transparent components are possible, different material properties can be combined on one component. Flexible and also rubber-like components are possible. Stable or multicolored components are also possible. Very fast manufacturing process.
Disadvantages: the heat resistance of the components is limited for several materials. High manufacturing costs.
Material: various photopolymer materials which are hardened by UV light. Many different types of plastic and rubber can be simulated.
Vacuum casting (VAG)
Advantages: high level of accuracy, smooth surfaces are possible, transparent and single-color models are possible, the most complex shapes are possible, cost-effective silicone rubber mold.
Disadvantages: rapid wear of the mold, the heat resistance of the components is limited due to the silicone mold. Only economically applicable for a certain number of components.
Material: two-component casting resins, wax materials.
Metal printing (Bound Metal Deposition – BMD)
Advantages: more homogeneous surface compared to cast parts, high stability, high component density, alternative to “MLS” – metallic laser sintering, metallic RP process suitable for offices.
Disadvantages: limited suitability for larger quantities, several process steps are necessary until the finished component
Material: stainless steel, alloy steel, aluminum alloys, tool steel, nickel, copper and much more
3D paper printing (Selective Deposition Lamination – SDL)
Advantages: Multicolored components can be produced with high resolution, cost-effectively and in an environmentally friendly manner.
Disadvantages: The components can only be loaded to a limited extent, display models are primarily produced using this process.
Materials: Standard DIN paper.
3D foil printing (Laminated Object Manufacturing – LOM)
Advantages: low production costs.
Disadvantages: poor manufacturing and detail accuracy, monochrome, due to the limited areas of application, this technique is hardly used anymore.
Materials: paper, plastic, aluminum.
If you have further questions about the individual technologies or need support with a project, please feel free to contact us. We will help you in the best possible way, as we are the 3D printing service provider for all 3D printing topics in the rapid prototyping sector. We help you with product development, the selection of the most suitable manufacturing process and the manufacture of your components.